AI in Manufacturing: Myths Busted, Facts Revealed
Recent Post:

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s a reality reshaping industries worldwide, and manufacturing stands at the forefront of this revolution. As industrial IoT and smart factories advance, the manufacturing industry produces enormous amounts of data daily. This influx of information, combined with increasingly sophisticated technologies such as machine learning (ML) and deep learning, reveals previously unchallenged potential for manufacturing processes' automation, accuracy, and effectiveness.
Nevertheless, misunderstandings of AI in manufacturing are still prevalent, leading to reluctance to use it. These myths tend to obscure the material benefits, e.g., predictions of failures leading to minimal downtime or AI-based intelligence leading to better demand forecasting and less waste.
This blog will dispel these myths and present a clear, fact-based picture of how AI empowers manufacturers to innovate, optimize, and lead in an ever-evolving industrial landscape. Whether you are an industrial expert or a technology geek, this guide will illuminate AI use cases in manufacturing.

Why is AI Essential for Modern Manufacturing?
AI is the heart of Industry 4.0, the process of robotisation, and the datafication of manufacturing. It has the potential to free the best latent information contained in the vast volumes of data churned out by companies' production lines. With machine learning and predictive analysis, AI can enhance workflows, reduce downtime, and produce higher-quality products, resulting in efficient, precise, and innovative production lines. It provides context on data processing and manipulation dynamics and its analysis. It enables manufacturers to respond quickly to market changes, improve safety by identifying risks and, in turn, carry out better supply chain management for increased efficiency. Due to the production process revolution, AI ensures competitiveness and sustainable future growth in a constantly changing industrialised society of automation.
Myth 1: AI Will Replace Human Workers Entirely
Fact: AI Enhances Human Roles, Not Eliminates Them
The widespread fear of AI-enabled job displacement is not unfounded, but AI in manufacturing is also essentially a matter of augmentation, not replacement. AI methods also automate routine tasks, freeing human workers to focus on tasks of more excellent value, including decision-making, creativity, and problem-solving.
For instance, predictive maintenance using AI can decrease equipment unavailability, but human technicians still need to read what can be gathered and perform the associated repairs. Similarly, robots with artificial intelligence capabilities can assemble parts, but only if they are programmed and optimised under the supervision of a human programmer.
Myth 2: AI Is Only for Large-Scale Manufacturing
Fact: AI Solutions Are Scalable and Accessible
The perception that AI is only available to large corporations with huge expenditures is wrong. AI technology is becoming available to small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
Cloud-based and Software-as-a-service (SaaS) models of artificial intelligence (AI) platforms can enable firms to implement AI with limited capital front-end investment. For example, SMEs can apply AI to inventory management, supply chain optimization, and production process improvement without custom infrastructure.
Myth 3: AI Is a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
Fact: AI Requires Tailored Implementation
However, no universal plug-and-play AI-based system applies to all industrial processes. All applications must be adapted depending on the subject's needs, goals, and data.
Specifically, in the case of defects detection, an artificial intelligence (AI) system is relevant for the food industry but not for the automotive industry, because operation parameters and databases of those are different). Tailored AI implementation ensures higher accuracy and relevance.
Myth 4: AI Guarantees Immediate Results
Fact: AI Implementation Takes Time and Refinement
But with a price, the full realisation of AI's promise is realized. Training AI models depends on high-quality training and input examples, algorithmic checking, and model tuning to ensure operational efficiency.
Myth 5: AI Always Involves Complex Technologies
Fact: AI Can Be Simplified for Everyday Use
AI is only sometimes sophisticated robots or intelligent neural networks. In manufacturing, AI, in its simplest possible form, can be a solver-like tool, etc.
For example, prediction analytics is used by AI-enabled software applications for stocking control and production planning. These enabling tools are so simple that developing skills for employees with no technical background and building AI's potential into them is possible.
Myth 6: AI Compromises Data Security
Fact: AI Can Strengthen Security Measures
The worries about AI and data breaches are legitimate but are often overblown. Suitable handling can help AI to improve cybersecurity by detecting anomalies, predicting attacks, and reacting to vulnerabilities in real-time.
Industrially, AI defends intellectual property and upholds industry standards. Implementing secure AI technologies that are sufficiently encrypted and governed avoids risks.
Myth 7: AI Is Too Expensive to Implement
Fact: AI Provides Long-Term ROI
Nevertheless, long-term cost savings and efficiency gains, which are expected to increase, will probably outweigh the initial investment. Applying AI to waste prevention, resource optimization, and increased manufacturing efficiency translates to a good return on initial invested cost (ROI).
For example, predictive maintenance based on AI rarely leads to equipment failure and artificial intelligence-based quality control rarely leads to defects, consequently saving time and money.
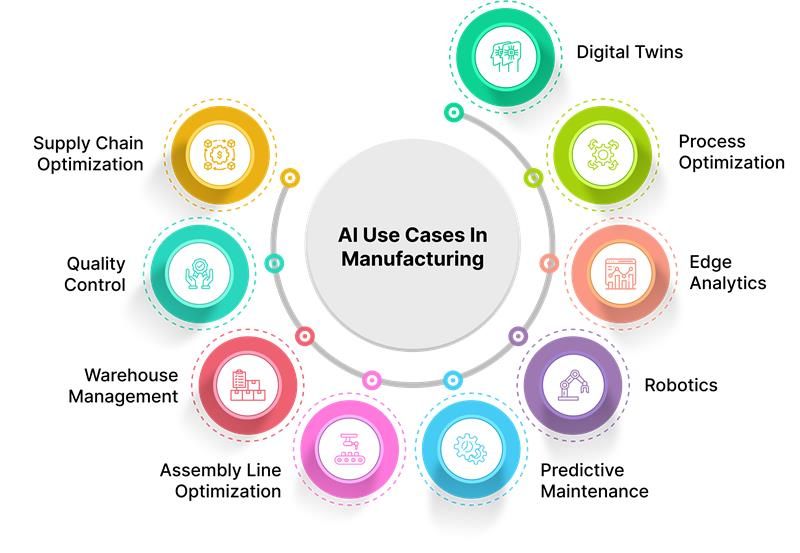
Top AI Use Cases In Manufacturing:
1. Supply Chain Optimization
AI helps increase supply chain performance by optimizing demand forecasting, inventory management, and planning/allocation, achieving timely delivery and reducing operation costs.
2. Quality Control
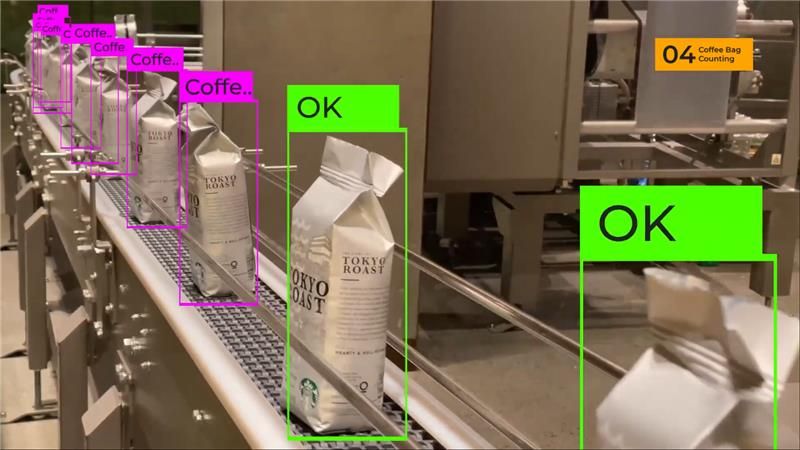
AI-based visual inspection systems detect defects online, enabling higher product quality, reduced waste generation, and more homogeneous production lines.
3. Warehouse Management
Using artificial intelligence, warehouses can be improved by tracking efficient stocks, automating storage areas, and ensuring fast order delivery.
4. Assembly Line Optimization
AI-enabled solutions for this task, based on production data, help optimize assembly line efficiency, eliminate bottlenecks, and improve throughput.
5. Predictive Maintenance
AI platforms can measure and analyze machine data to predict machine failures, preventing system failures, prolong machine life, and reducing maintenance costs.
6. Robotics
Robot systems based on artificial intelligence (AI) have advantages in automatic working, accuracy in complex tasks, and workplace safety through synergic work with human beings.
7. Edge Analytics
Edge analytics is used in manufacturing to compute runs on the devices/sensors that generate the data and improve actionable intelligence faster.
- Improving production quality and yield.
- Early recognition of performance degradation and breakdown of equipment.
- Monitoring worker health and safety through wearable devices.
8. Process Optimization
Production workflows are scanned by AI so that issues of inefficiency can be pinpointed, resources can be bettered, and, in turn, manufacturing processes can be streamlined.
9. Digital Twins
Using AI, digital twins, virtual replicas of real-world physical systems can be created for real-time simulation, monitoring, and optimization of manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
AI is reshaping manufacturing, dispelling myths, and driving innovation. It complements human work, provides solutions for huge, as well as for small and large volume commercial companies, and, in the future, drives efficiency, quality improvement, and cost reduction. It is not a replacement for work or too high in complexity, but AI also offers manufacturers tools for automation of work, safety operation and survival in competition. The current use of AI gets us closer to a smarter, greener industrial future.
Comment
0Comments
No comments yet.


